Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (35): 5718-5726.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1482
Previous Articles Next Articles
Systematic review and meta-analysis of effect of resistance exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Liang Min1, Wang Hainiu2, Huang Peng2, Zhu Weihua2, Li Shunchang1
- (1Institute of Sports Medicine and Health, 2College of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China)
-
Online:2019-12-18Published:2019-12-18 -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Program of Sichuan Province, No. 2018JY0499 (to LSC); the Project of Sichuan Provincial Key Laboratory for Sports Medicine, No. 2018-A009
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Min, Wang Hainiu, Huang Peng, Zhu Weihua, Li Shunchang . Systematic review and meta-analysis of effect of resistance exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5718-5726.
share this article
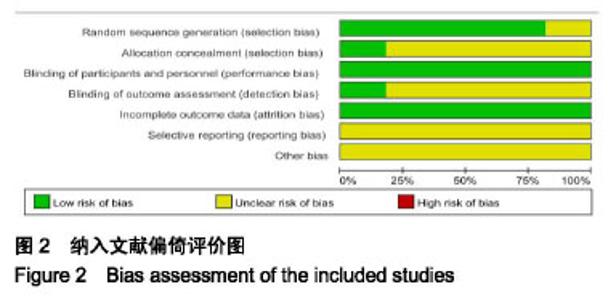
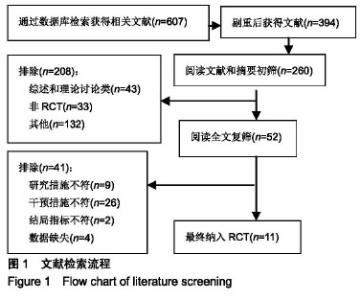
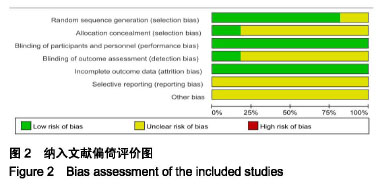
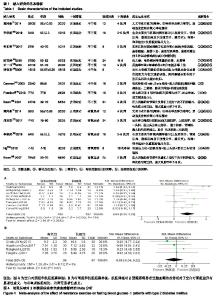
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 见表1。 2.3 纳入文献的方法学质量评价 纳入文献信息对照Cochrane系统评价标准分别从随机分组产生、隐藏分组、双盲实验、效应指标盲检、实验数据不完整、实验结果的选择性报告、其他偏倚风险等7个评价指标对纳入文献偏倚风险进行综合评价。图2为纳入文献偏倚评价,图3为纳入文献的风险总结图。总体分析,纳入文献存在一定的偏倚风险。其中Canmen隐藏分组和效应指标盲检评估为不清楚;Ng CL和Plotnikoff RC的文献质量很高,偏倚风险较低;Ronald J、周欢欢、李荣娟、欧雪群、理同新和许东明的隐藏分组和效应指标盲检评估为不清楚;王一书的和谭俊珍的研究由于未明确提出试验按照随机分配原则进行分组,故随机分组产生项的评估为不清楚;所有文献均未采用双盲,因受试者对干预手段不能采用盲法操作;试验结果的选择性报告和其他偏倚风险指标由于其独特性,所有文献的该两项评估均为不清楚,但整体文献质量处于中等偏上。 "
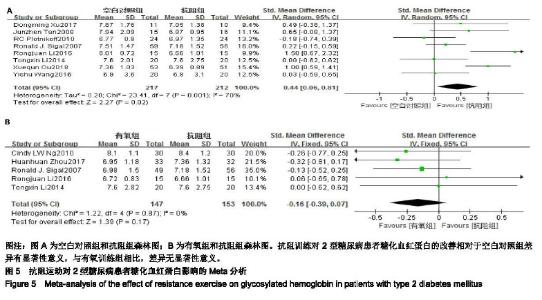
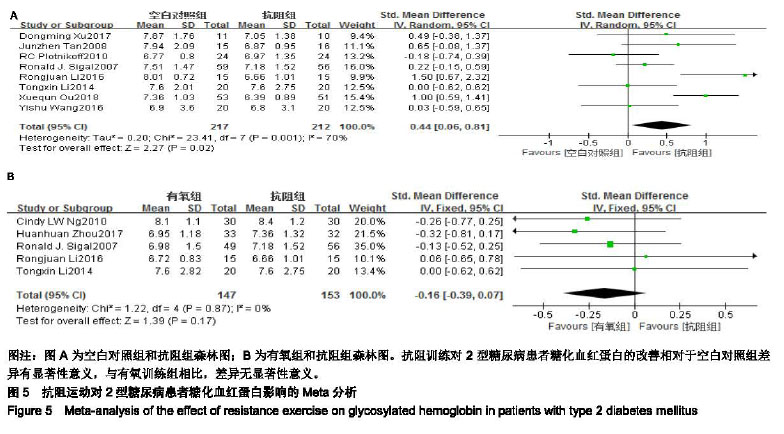
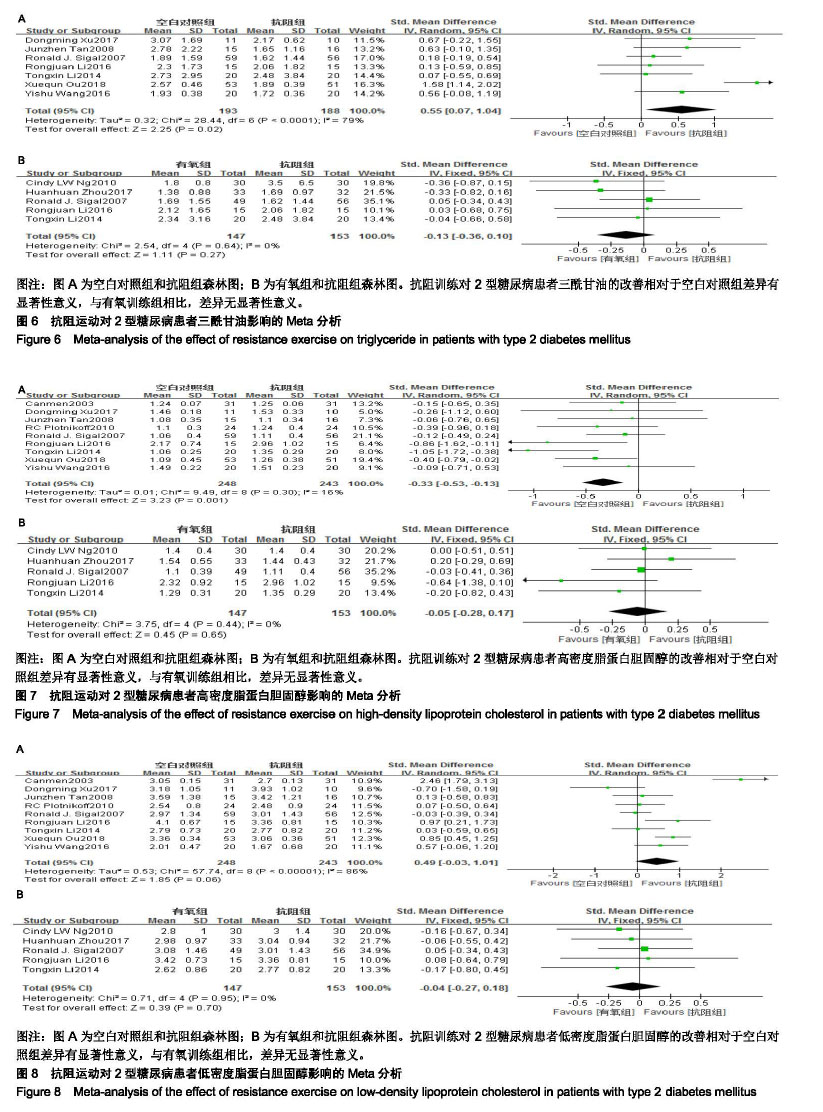
2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者空腹血糖的影响 空白对照与抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者空腹血糖影响研究共纳入8个RCTs[9-16],各研究间存在统计学异质性(χ2=27.94,I2=75%,P=0.000 2),因此通过随机效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,相对于空白对照组,抗阻训练对2型糖尿病患者空腹血糖的改善差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.84,95%CI(0.39,1.29),P=0.000 2,见图4A]。 有氧运动与抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者空腹血糖影响研究共纳入4个RCTs[9-10,17-18],各研究间不存在统计学异质性(χ2=1.29,I2=0%,P=0.73) ,因此通过固定效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,与有氧训练组相比,抗阻训练对于空腹血糖的改善差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.06,95%CI(-0.34,0.22),P=0.67,见图4B]。 2.4.2 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白的影响 空白对照与抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白影响研究共纳入8个RCTs[9-14,16,19],各研究间存在统计学异质性 (χ2=23.41,I2=70%,P=0.001),因此通过随机效应模型进行 Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,相对于空白对照组,抗阻训练对2型糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白的改善差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.44,95%CI(0.06,0.81),P=0.02,见图5A]。 有氧运动与抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白影响研究共纳入5个RCTs[9-10,17-19],各研究间不存在统计学异质性(χ2=1.22,I2=0%,P=0.87),因此通过固定效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,与有氧训练组相比,抗阻训练对于糖化血红蛋白的改善差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.16,95%CI(-0.39,0.07),P=0.17,见图5B]。 2.4.3 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者三酰甘油的影响 空白对照与抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者三酰甘油影响研究共纳入7个RCTs[9-14,19],各研究间存在统计学异质性(χ2= 28.44,I2=79%,P < 0.000 1), 因此通过随机效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,相对于空白对照组,抗阻训练对2型糖尿病患者三酰甘油的改善差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.55,95%CI(0.07,1.04),P=0.02,见图6A]。 有氧运动与抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者三酰甘油影响研究共纳入5个RCTs [9-10,17-19],各研究间不存在统计学异质性(χ2=2.54,I2=0%,P=0.64) ,因此通过固定效应模型进行 Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,与有氧训练组相比,抗阻训练对于三酰甘油的改善差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.13,95%CI(-0.36,0.10),P=0.27,见图6B]。 "


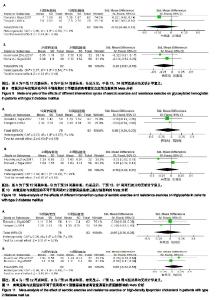
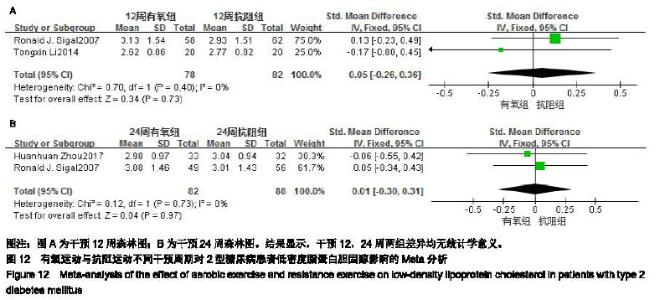
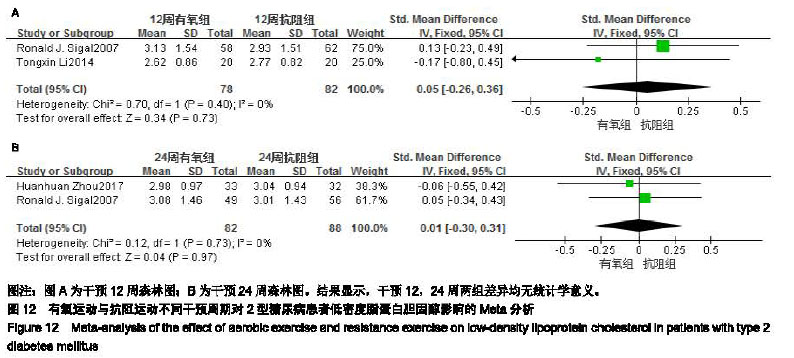
2.4.4 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者高密度脂蛋白胆固醇的影响 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者高密度脂蛋白胆固醇影响研究共纳入9个RCTs[9-16,19],各研究间不存在统计学异质性(χ2=9.49,I2=16%,P=0.30),因此通过固定效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,相对于空白对照组,抗阻训练对2型糖尿病患者高密度脂蛋白胆固醇的改善差异有显著性意义[SMD=-0.33,95%CI(-0.53,-0.13),P= 0.001,见图7A]。 有氧运动与抗阻运动与对2型糖尿病患者高密度脂蛋白胆固醇影响研究共纳入5个RCTs[9-10,17-19],各研究间不存在统计学异质性(χ2=3.75,I2=0%,P=0.44) ,因此通过固定效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,与有氧训练组相比,抗阻训练对于高密度脂蛋白胆固醇的改善差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.05,95%CI(-0.28,0.17),P=0.65,见图7B]。 2.4.5 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的影响 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者低密度脂蛋白胆固醇影响研究共纳入9个RCTs[9-16,19],各研究间存在统计学异质性(χ2=57.74,I2=86%,P < 0.000 01),因此通过随机效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,相对于空白对照组,抗阻训练对2型糖尿病患者低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的改善差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.49,95%CI(-0.03,1.01),P=0.06,见图8A]。 有氧运动与抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者低密度脂蛋白胆固醇影响研究共纳入5个RCTs[9-10,17-19],各研究间不存在统计学异质性(χ2=0.71,I2=0%,P=0.95) ,因此通过固定效应模型进行Meta分析。Meta分析结果显示,与有氧训练组相比,抗阻训练对于低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的改善差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.04,95%CI(-0.27,0.18),P=0.70,见图8B]。 2.5 有氧运动与抗阻运动不同干预周期的亚组分析 2.5.1 有氧运动与抗阻运动不同干预周期对2型糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白的影响 2篇文献报道了干预12周的结 果[9,19],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.16,95%CI(-0.48,0.15),P=0.30,见图9A]。2篇文献报道了干预24周的结果[12,17],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.20,95%CI(-0.51,0.10),P=0.18,见图9B]。 2.5.2 有氧运动与抗阻运动不同干预周期对2型糖尿病患者三酰甘油的影响 2篇文献报道了干预12周的结果[9,19],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异无统计学意义。[SMD=-0.08,95%CI(-0.39,0.23),P=0.59,见图10A]。2篇文献报道了干预24周的结果[12,17],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.10,95%CI(-0.40,0.21),P=0.53,见图10B]。 2.5.3 有氧运动与抗阻运动不同干预周期对2型糖尿病患者高密度脂蛋白胆固的影响 2篇文献报道了干预12周的结果[9,19],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异显著性意义[SMD=-0.05,95%CI(-0.36,0.26),P=0.76,见图11A]。2篇文献报道了干预24周的结果[12,17],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.06,95%CI(-0.24,0.36),P=0.69,见图11B]。 2.5.4 有氧运动与抗阻运动不同干预周期对2型糖尿病患者低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的影响 2篇文献报道了干预12周的结果[9,19],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.05,95%CI(-0.26,0.36),P=0.73,见图12A]。2篇文献报道了干预24周的结果[12,17],亚组分析结果显示,两组差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.01,95%CI(-0.29,0.31),P=0.95,见图12B]。 "
| [1]International Diabetes Federation.IDF Diabetes Atlas-7th Edition.Diabetes Atlas http://www.diabetesatlas.org/,2015.[2]Holman N , Young B, Gadsby R. Current prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults and children in the UK. Diabet Med. 2015; 32(9):1119-1120.[3]Strasser B,Pesta D.Resistance training for diabetes prevention and therapy: experimental findings and molecularmechanisms. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:805217. [4]李蕙.糖尿病治疗的"五驾马车"在妊娠糖尿病患者中的应用[J].实用临床医药杂志,2009,5(16):19-25.[5]江山,李胜楠,朱登月,等.抗阻运动在2型糖尿病患者康复应用的研究进展[J].糖尿病新世界,2018, (8):196-197.[6]王静,刘欣,王晶晶.抗阻运动对2型糖尿病的作用及机制研究进展[J].上海体育学院学报,2015,36(4):70-73.[7]贺佳佳.等速肌力运动和有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者血糖急性效应的研究[D]. 南京:东南大学,2013.[8]Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al.The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343(d5928):1-9.[9]理同新.不同运动干预对2型糖尿病患者血液生化指标的影响[J].山东体育科技,2014,36(6):81-84.[10]李荣娟,李锋.不同运动方式对2型老年男性糖尿病患者血糖?血脂等指标的影响研究[J].广州体育学院学报.2017,37(2):99-101.[11]许东明.离心训练对2型糖尿病人群干预作用的研究[D].曲阜:曲阜师范大学,2017.[12]欧雪群,莫喜萍,覃美凤,等.抗阻力运动联合穴位按摩对老年糖尿病病人生理指标的影响[J].护理研究,2018,32(4):583-586.[13]王一书,殷显德,王海峰,等.抗阻运动对老年2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢的临床研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2016,20(5):733-735.[14]谭俊珍,李平,潘建明,等.力量训练对2型糖尿病的干预作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2008,28(12):1103-1104. [15]Castaneda C, Layne JE, Munoz-Orians L, et al.A randomized controlled trial of resistance exercisecontrol in older adults with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(12): 2335-2341. [16]Plotnikoff RC, Eves N, Jung M, et al.Multicomponent, home-based resistance training for obese adults with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010; 34(12):1733-1741.[17]周欢欢.抗阻运动对改善2型糖尿病患者心血管风险的效果研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2017.[18]Ng CL, Goh SY, Malhotra R, et al.Minimal difference between aerobic and progressive resistance exercise on metabolic profile and fitness in older adults with diabetes mellitus: a randomised trial. J Physiother. 2010;56(3):163-170.[19]Baum K, Votteler T, Schiab J. Efficiency of vibration exercise for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Int J Med Sci. 2007; 4(3):159-163.[20]陈伟伟,高润霖,刘力生,等.中国心血管病报告2013概要[J].中国循环杂志, 2014,29(7):487-491.[21]Gross JL,de Azevedo MJ,Silveiro SP,et al.Diabetic nephrop? athy:diagnosis,prevention,and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005;28: 164-176.[22]Miele EM,Headley SAE.The effects of chronic aerobic exercise oncardiovascular risk factors in persons with diabetes mellitus . CurrDiab Rep.2017;17(10): 97.[23]American Diabetes Association.Classification and Diagnosis of Diabe-tes.Diabetes Care.2016;39(1):13-22.[24]Nery C,Moraes SRA,Novaes KA,et al.Effectiveness of resistance ex-ercise compared to aerobic exercise without insulin therapy in patientswith type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta- analysis.Braz J Phys Ther.2017;21(6):400-415.[25]Grace A, Chan E, Giallauria F, et al. Clinical outcomes and glycaemicresponses to different aerobic exercise training intensities in type II dia-betes: a systematic review and meta- analysis . Cardiovasc Diabetol.2017; 16(1): 37.[26]聂荣彪,王岐富.Ⅱ型糖尿病运动疗法的研究[J].当代体育科技, 2014,4(31):212-213.[27]Junfen F,Li L,Chunxiu G,et al. Chinese childrens’diabetes status,trends and hardship.Int J Pediatr Endocrinol.2013;(1):13.[28]Bweir S, Al-Jarrah M, Almalty AM, et al.Resistance exercise traininglowers HbA1c more than aerobic training in adults with type 2 dia-betes.Diabetol Metab Syndr.2009;1 (27) :1-7.[29]Praet SFE,van Loon LJC.Exercise therapy in Type 2 diabetes.Act Diabetologica.2009;46(4):263-278.[30]Bweir S, Al-Jarrah M, Almalty AM,et al.Resistance exercise training lowers HbA1c more than aerobic training in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr.2009;1:27. [31]Zanuso S,Jimenez A,Pugliese G,et al.Exercise for the management of type 2 diabetes: a review of the evidence. Actadiabetologica. 2010;47(1): 15-22.[32]杨中方,白姣姣,李全磊,等.抗阻力运动对2型糖尿病患者血糖控制效果的Meta分析[J].护理学杂志,2014,29(3):81-84.[33]吴志建,王竹影,宋彦李青.不同运动处方对2型糖尿病患者改善效果的Meta分析[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(1):73-82. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||